
#Centos 7 static ip example software
You'll need the IP address if you're hosting server software – the client computers will need your computer's IP address to connect to it. Your computer likely has public and private IP addresses. And you'll need to know that computer's private IP address so you can configure your router to direct that kind of traffic to the right computer on your local network. You'll need to know your network's public IP address that people can type into their client software. Maybe you're playing a multiplayer game, maybe you need to access a home-hosted media server, or maybe you just want to get remote access to one of your PCs. Say you're hosting some kind of server software on a computer on your network and you need people on the Internet to be able to connect to it. Sometimes, you might need to know the private IP address of a device or your network's public IP address-or maybe both.
#Centos 7 static ip example how to
RELATED: How to Access Windows Remote Desktop Over the Internet Note that if your computer is connected directly to the Internet with no router sitting in between-something we really don't recommend-your computer's IP address is a public IP address. From an outside perspective, all devices on the home network are communicating with the Internet from a single public IP address. The router acts as an intermediary, forwarding traffic to the local IP addresses that request it. The computers, smartphones, game consoles, and other devices behind the router each have a unique private IP address on the home network. In a typical home network, a router has a public IP address on the Internet. The answer to all this IP address wizardry is that your router-whether it's a standalone device or a modem/router combo unit-essentially serves as a bridge between two networks. RELATED: What's the Difference Between a Modem and a Router?

So, how does that all work and how can you find out what all those IP addresses are? Read on for the answer! Public vs. But, you've likely got multiple computers and other devices on your network-each of which needs its own IP address. This address is how you communicate with all the other devices out there on the public Internet. When you sign up with Internet service and connect your modem, your ISP assigns you a public IP address. Here's how that works and how you can find those IP addresses.Īn IP address (or Internet Protocol address) identifies each networked computer and device on a network.
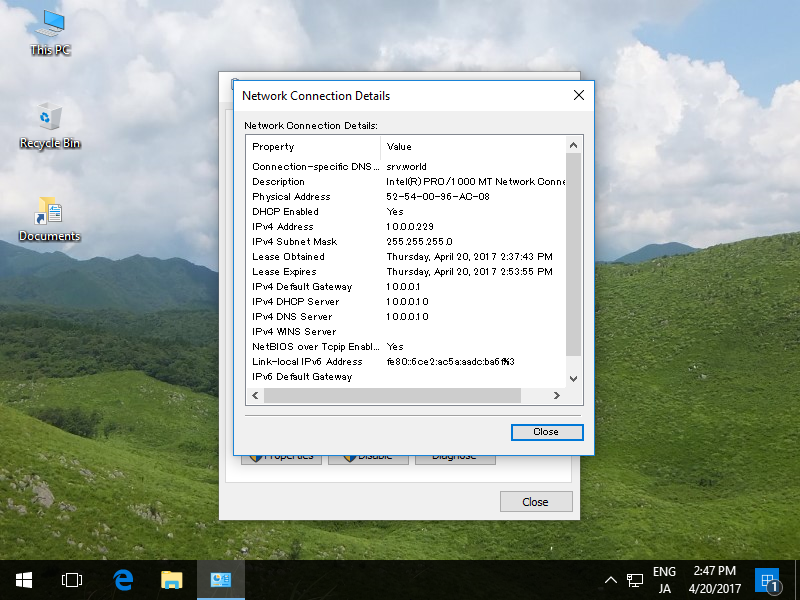
But your ISP assigns you a public IP address that other devices on the Internet can see. Each device on your network has a private IP address only seen by other devices on the local network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
